Pyogenic granuloma, although the term may sound alarming, is a common and benign growth that can occur in the oral cavity. Understanding this condition, its causes, identification, treatment options, and its impact on oral health is crucial for individuals and professionals alike.
Introduction to Pyogenic Granuloma
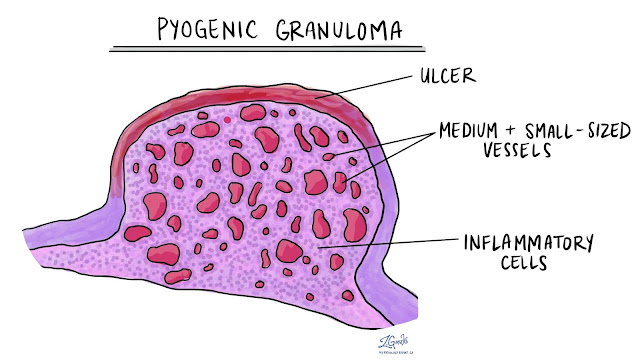
Pyogenic granuloma, also known as lobular capillary hemangioma, is a non-cancerous, vascular lesion that typically appears as a red, raspberry-like nodule in the mouth. It often emerges on the gums but can occur anywhere in the oral cavity.
Understanding Pyogenic Granuloma
The formation of pyogenic granuloma is often linked to local irritation or trauma to the soft tissues in the mouth. Despite its name, it is not an infection but rather an exaggerated response of blood vessels to minor injury.
Occurrence and Prevalence
While anyone can develop pyogenic granuloma, certain factors, such as pregnancy, hormonal changes, poor oral hygiene, or certain medications, might increase the risk.
Causes and Risk Factors
Various factors contribute to the development of pyogenic granuloma, including:
- Trauma or Injury: Constant irritation or trauma to the gums or oral tissues.
- Hormonal Changes: Occurrence during pregnancy or due to hormonal fluctuations.
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate dental care leading to gum irritation.
- Medications: Certain medications may trigger its formation.
Associated Conditions
Pyogenic granuloma might accompany other conditions like gingivitis or periodontitis, impacting overall oral health.
Symptoms and Identification
Identifying pyogenic granuloma includes observing:
- Visual Signs: Red or pink nodules on the gums or oral mucosa.
- Physical Symptoms: Bleeding or tenderness around the affected area.
Diagnosis and Medical Examination
Dental professionals diagnose pyogenic granuloma through visual examination and might opt for a biopsy to confirm the diagnosis.
Methods for Diagnosis
Biopsy and histopathological examination are commonly employed for accurate identification.
Consultation and Evaluation
Consulting with a dentist or oral surgeon is imperative for a comprehensive evaluation.
Also Read: Herbs That Lower Blood Sugar Fast
Treatment Options
Treatment options include:
- Surgical Approaches: Surgical excision or laser removal.
- Non-Invasive Treatments: Cryotherapy or topical medications.
Recovery Process and Aftercare
Following treatment, proper aftercare is essential to prevent recurrence and address any potential complications.
Post-Treatment Care
Maintaining good oral hygiene and following post-operative instructions are crucial for recovery.
Potential Complications
While rare, complications such as recurrence or infection might occur post-treatment.
Preventive Measures
Implementing preventive measures involves:
- Lifestyle Changes: Optimal oral hygiene practices and avoiding irritants.
- Monitoring and Follow-Ups: Regular dental check-ups for early detection.
Addressing Common Misconceptions
Dispelling myths surrounding pyogenic granuloma can alleviate unnecessary concerns.
Debunking Myths
Misconceptions about its contagiousness or association with poor hygiene need clarification.
Clarifying Misunderstandings
Educating individuals about its benign nature and manageable treatment options is crucial.
Impact on Oral Health
Pyogenic granuloma's presence can influence:
- Oral Hygiene Concerns: Challenges in maintaining oral cleanliness.
- Long-term Oral Health Effects: Potential impacts on gum health and tooth stability.
Psychological Impact
Dealing with such oral growths can evoke emotional responses.
Emotional Aspects
Feelings of concern or anxiety are common, requiring emotional support.
Coping Strategies
Counseling or support groups can aid in coping with the emotional toll.
Research and Advancements
Recent studies and developments in treating pyogenic granuloma show promise.
Recent Studies
Ongoing research explores new treatment modalities and prevention strategies.
Promising Developments
Advancements in minimally invasive treatments offer hope for improved management.
Patient Experiences and Stories
Real-life accounts of individuals dealing with pyogenic granuloma provide insights.
Real-life Accounts
Sharing experiences and lessons learned from managing the condition can inspire others.
Insights and Learnings
Understanding personal journeys can provide valuable lessons for patients and caregivers.
Professional Insights and Perspectives
Expert opinions and recommendations shed light on effective management.
Expert Opinions
Dental professionals offer insights into the best practices for diagnosis and treatment.
Medical Recommendations
Guidelines and recommendations from medical associations aid in standardizing care.
Community Support and Resources
Accessing support groups and online resources can provide invaluable assistance.
Support Groups
Engaging with others facing similar challenges fosters a sense of community.
Online Platforms and Resources
Utilizing online platforms with reliable information aids in navigating the condition.
Conclusion
Pyogenic granuloma, though unsettling, is manageable with proper diagnosis and treatment. Understanding its nuances, treatment options, preventive measures, and its impact on oral health is pivotal for individuals and healthcare providers. Dispelling myths, offering emotional support, and staying updated on advancements are integral to effectively managing this condition.
FAQs
Is pyogenic granuloma contagious?
- No, it is not contagious and does not spread from person to person.
Can pyogenic granuloma be prevented?
- Maintaining good oral hygiene and avoiding irritants can help prevent its occurrence.
Are there any long-term complications of pyogenic granuloma?
- While rare, complications like recurrence or infection might occur post-treatment.
Is surgery the only treatment option for pyogenic granuloma?
- No, non-invasive treatments like cryotherapy or topical medications are also available.
What should one do if they suspect they have pyogenic granuloma?
- Consulting a dentist or oral surgeon for proper evaluation and diagnosis is recommended.